In conjunction with rising remote work alongside with COVID19 pandemic, cyber-attacks and breaches have increased. But still, most individuals and companies aren’t prepared enough for cyberattacks. By the following basic tips about personal cybersecurity, this article aims to help you increase your ability to protect yourself against the sophisticated hackers’ techniques that continue to evolve. Let’s explore…
#1. Self-awareness Role and Precaution
Despite that, programmers and software producers are very careful to protect the end-users, but personal cybersecurity is similar to your house door lock. Though many police are caring to protect you, you should also lock your house door yourself. As well, cybersecurity also is everyone’s responsibility. You should take care of being cognitively updated. Most cybersecurity issues depend on updating your knowledge about the newest hacking and malware trends. In many cases, cyberthreats’ success was due to ignorance or negligence of some simple security tips.
#2. Understanding Digital Identity and the Nature of the Cyberworld
On the internet, you have many different digital identities than your one real-world identity. In the cyber world, you should enter your digital identity qualities in the form of credentials to identify you as the owner of the device/account, so you need to protect these credentials carefully. It resembles your real-life credentials, face, sound, and national identity card, etc. So if attackers have known your cyberworld credentials which usually can be your username and password, you have fallen prey to them. They will have access to your private messages and photos in your social media account or your bank account details and money.
#3. Enable Automatic Security Updates
For your devices’ software, from the operating system (Windows, Android, Mac, etc.) to the browser extension, you should set every application and software on your devices to the auto-update option. Updating software adds new features and enables software companies to fix bugs and remove critical vulnerabilities that hackers exploit to make their attacks. Despite the horror generated by the increase of cyber threats, by updating your every software, you have nearly half of the way towards enjoying secure computing and internet browsing. In addition to that, you need to update regularly your Antivirus and Firewall applications. This was well known for a long time on the PCs, but it’s newly become also recommended for smartphones, though phones still don’t make installing Antivirus mandatory as in Windows OS. The benefits of updating protection software are to keep them with the latest trends of cyberattacks. This helps protect your devices from new malicious files and viruses effectively and keeps your data safe from attacks that damage or steal them. Antivirus is not just for personal computers but also business.
#4. Avoid Sharing and Clicking Unknown Links
Clicking anywhere without investigating the website’s legitimacy or downloading an attachment without knowing the email sender may cause entering malicious software into your device. It may be an infected URL that causes installing ransomware that locks your access to your data unless you pay money for the hacker. Also, it’s recommended to install some browser plugins that block automatic downloading of any scripts or Java, whereas flash plug-in content can host malicious code. Regarding sharing, you shouldn’t disclose your password and sensitive information to anyone. Also, when you use multifactor authentication that combines multiple types of credentials, face, fingerprint, SMS based authentication to your phone with a one-use code, don’t give this SMS code to any person. For example, some attackers ask you to give them this code to join you for a Whatsapp group, don’t give them. In general, experts said sharing is not caring, not only for your credentials but even for much of your personal information. It’s recommended to share the minimum amount of personal information on social media. Besides, Check your privacy settings on all of your social media accounts, especially on Facebook.
#5. Avoid Setting Easy-to-discover Password
Password should be easy to remember, but this makes it easy to discover! Attackers use dictionary-based software to try from millions of possibles and the most commonly used passwords. Please avoid specifically those top 200 easy passwords easy to discover. Besides, don’t use your name, family name, birthday, or personal thing as a password; hackers can make unexpected investigations about your life. How to make a password that is easy to remember for you and impossible to discover for hackers? It would be best if you made a complex password, but in a way that you can remember it. For example, take the first letters of some quotes; this makes them a new nondictionary word. Then modify it with some numbers and symbols to increase its power. The password also should be a long one. And it would help if you used a different password for every different login, so you need Password Manager software. It makes you need only to remember one long password for all your logins, and it’s called the Master Password.
#6. Be Aware of Social Engineering Deceiving Methods
Social Engineering is used typically in marketing and politics. But in the cyberworld, it’s used sometimes for hacking and deception. By gaining your confidence to give them some of your credentials, they trick you into breaching your data. It’s become easier with the smartphone. Recently, the number of cyber-attacks has increased since using the smartphone. Social Engineering deceiving is not based on technology vulnerabilities but human or user behavior. Deceiving by Social Engineering existed before computers, but computers and smartphones make it easier to do. But we should not be afraid of using digital technology if we truly understand it. To avoid Social Engineering, be aware of some hidden self-biases. For example, you have an email claim that you should reply urgently in 24 hours to get your heritage and that you must give them your password or send them some money or your password. Some other example, when they are exploiting respect for an authority such as police or your boss to give them your password. In all cases, don’t give the password to anyone.
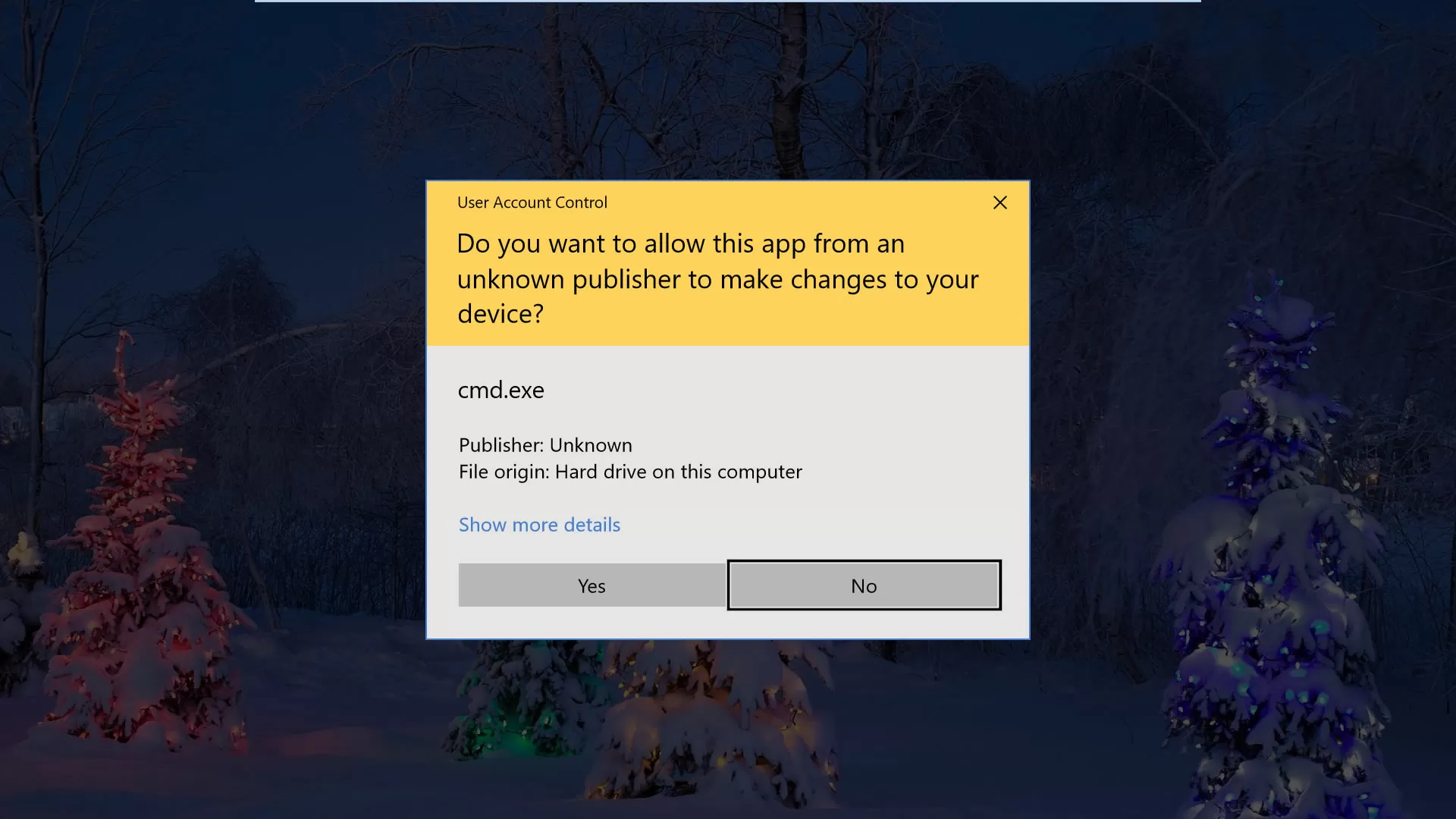
#7. Always install Your Apps From a Legitimate Software Store.
Ensure you download your apps and software from the original websites on the computer; avoid those modified or cracked. When you double click the installing (EXE) file, a message prompts on the Windows screen will tell you the publisher name of the software. If the message color is blue and the publisher’s name is stated, it’s OK. But if the publisher name is unknown and the message color is yellow, you should avoid installing this unknown publisher software; it’s maybe malware can harm your data. For your smartphone, always make sure to install only from legitimate secure stores, such as Google Play, Samsung Store, App Store. And avoid enabling installing apps from third-party sources.
#8. Check the Email Address and the Link Domain Name
When you receive an email or open an URL, you should make sure of the domain name and the sender’s email address. For example, you may open some URL that appears as a genuine-looking Facebook website. But if you check the domain name above in the domain box, you may find something like “facebook.example.com”. This is not the Facebook original domain name, or you may find something different such as faceboök.com; notice here is a different (o) letter. The same applies to the email address. These fake domains/email address aims to deceive and phishing you. With the fake Facebook URL, if you log in entering your username and password, the hacker on the other side will take them and will hack your Facebook account. In the fake email case, they perhaps try to convince you to pay some money or give them some critical information claiming that they are from the Google security team or Paypal, etc. So, carefully check the email sender address.
#9. Distinguish Between Backup and Cloud Sync
Backing up is a vital security procedure even before the spread of the internet; it secures a copy of your sensitive data or even the entire system and software on an external disc or at the cloud. You can restore your data if it’s damaged or compromised by some hacker, or even if just the device crashes. There are many backup software and hardware options, and automatic backup is the best. Some of them work on your local device and store the backup on an external disc, which doesn’t need high-speed internet. Some others upload your data to the cloud, be aware that cloud sync is not a backup; in the cloud sync, you have a mirror of your files and data. So, when it’s modified or deleted from your device, it also will be deleted at the cloud. But some cloud services give you the ability to restore your files.
#10. Learn About Using Wi-Fi Safely
People tend to love using free public Wi-Fi. When you use it, keep in mind that it’s a fertile environment for hackers to steal your sensitive information or even get access to your smartphone/laptop. You can use it for watching some videos or surfing generally on the internet, but avoid entering login conditionals to any of your accounts. In some other advanced cases, you may surprise that your smartphone is still connected to your home Wi-Fi router even after you go to a far place from your home. Be very aware; it’s maybe another fake Wi-Fi network near you that emulates the same name and password as your home Wi-Fi. It’s aiming to break through your smartphone. Some people may think they are still connected to the same home Wi-Fi router somehow, but that is impossible for long distances.
Conclusion
Now you should have understood some of the personal Cybersecurity basics. You should take a step ahead to deal with them, and as long as you remain awake and update your security tools and awareness, you are mostly on the safe side.

![]()